Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-26 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Greasing Used Excavators: Importance and Benefits
● Types of Grease Most Suitable for Used Excavators
>> Molybdenum Disulfide (Moly) Grease
● Key Properties to Look for in Excavator Grease
● Application Areas That Require Greasing in Used Excavators
● Grease Selection: Factors to Consider
● Greasing Routine: Best Practices for Used Excavators
● Common Greasing Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
● Maintenance and Inspection Cycle: Guidelines for Used Equipment
● Diagnosing Grease-Related Problems
● Troubleshooting and Upgrading Greasing Practices
● Advanced Greasing Recommendations: Preserving Used Excavator Value
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What kind of grease works best for used excavators?
>> 2. How often should I grease the main pivot points in my used excavator?
>> 3. Can wrong grease type damage my excavator?
>> 4. Is greasing needed before storing my used excavator?
>> 5. How do I confirm all lubrication points are properly greased?
Grease is one of the essential substances for maintaining the performance and longevity of heavy machinery such as used excavators. Effective lubrication shields critical components from excessive wear, corrosion, and mechanical failure, ensuring that equipment continues to deliver reliable service for companies like KeyChain Venture Co., Ltd., a leading supplier of high-performance buses and heavy-duty trucks for global markets. Correct grease selection and application are crucial, especially when working with used excavators whose parts may already show signs of operational stress and aging. This comprehensive guide expands upon the key considerations, types, and methods for using grease in used excavators, aiming to help operators and fleet managers extract maximum value from their machines.

Regular greasing plays a central role in preserving both the daily reliability and the long-term health of an excavator, particularly when the machine is not new. The benefits of a well-lubricated used excavator include:
- Reduced friction between moving parts, lowering the risk of overheating and wear.
- Protection against internal rust and corrosion, especially in high-moisture environments.
- Smoother operations, quieter pivots, and a more responsive hydraulic system.
- Fewer breakdowns, which translates into minimized downtime and reduced repair costs.
For operators of used excavators, these benefits are magnified, as older machines typically require more stringent maintenance practices to offset the effects of prior use.
Understanding the varieties of grease available makes it easier to match the product to your used excavator's needs. Each type brings unique advantages:
- Offers robust water-resistance and stability in wide temperature ranges.
- Suitable for almost all primary lubricating points in excavators, especially those exposed to harsh work conditions.
- Incorporates solid lubricants to withstand extreme pressure and shock-load points, such as bucket, stick, and boom pins.
- A go-to choice for older excavators that may have developed play or wear at pivotal joints.
- Exceptional at resisting corrosion and water washout, particularly important for excavators operating in wet or corrosive environments.
- Increased film strength for maximum surface protection.
Polyurea greases excel for certain bearings subject to high heat but are less used for general joint lubrication. Always defer to the manufacturer's guidelines when grease recommendations for specific parts of a used excavator differ.
When selecting grease for a used excavator, prioritize the following characteristics:
- Load-Carrying Capacity: Essential for machines carrying heavy loads; look for EP (Extreme Pressure) additives to safeguard surfaces under force.
- Water Resistance: Critical as excavators work in mud, rain, and damp environments; lithium complex and calcium sulfonate greases excel here.
- Adhesion: Grease should stick firmly to the component to resist displacement by vibration or water.
- High Dropping Point: The temperature at which grease begins to melt should exceed the likely operating temperature—crucial for high-output excavators.
Detailed attention to each lubrication zone will keep used excavators running smoothly. The primary spots include:
- Boom, dipper, and bucket pins
- Slewing ring and bearing
- Track and roller assemblies
- Swing gear and hydraulic joints
For used excavators, because of pre-existing wear, frequent and thorough greasing is even more critical to minimize metal-to-metal contact and prolong component life.

Consider the following before choosing and applying grease:
- Operating environment: High humidity, rain, or mud exposure calls for highly water-resistant greases.
- Average temperature: Match grease type to climate; low-temperature greases for cold, high dropping-point for hot environments.
- Manufacturer guidelines: The excavator's service manual should dictate the recommended formulas and intervals.
Used excavators may need more frequent greasing, with higher-performance products to compensate for aging seals or possible contaminant ingress.
Consistent greasing is vital for maintenance. Follow these procedures for optimal results:
1. Preparation
- Select the appropriate grease gun type and load with the recommended grease grade.
- Gather clean cloths and tools for cleaning grease fittings.
2. Cleaning
- Carefully wipe off all dirt and debris from grease points to avoid introducing contaminants.
- Inspect for any visible signs of damage, wear, or corrosion.
3. Application
- Affix the grease gun and inject grease until clean lubricant appears, indicating the removal of old or contaminated grease.
- For used excavators, confirm that grease reaches both ends of the pin and bush, as increased wear can create gaps.
4. Post-Application Checks
- Remove excess grease to prevent dust accumulation.
- Record greasing tasks in a maintenance log for tracking and warranty purposes.
A breach in routine, such as missing a lubrication point or using contaminated grease, can have faster negative consequences in used excavators than in new models.
Mistakes can reduce the effectiveness of lubrication and may accelerate equipment wear. Common missteps include:
- Over-greasing: Leads to seal blowout and excessive pressure buildup.
- Under-greasing: Leaves surfaces exposed to premature wear and corrosion.
- Wrong product choice: Using grease not suited to the component's function, load, or environment undermines its protective function.
- Neglect of dirty fittings: Always clean before application to avoid abrasive particles damaging internal surfaces.
Following recommended practices ensures the used excavator operates reliably and maintains resale value.
A robust maintenance cycle accounts for the needs of aging components. Suggestions include:
- Grease high-wear points like bucket and boom pins daily, especially after intense usage.
- Inspect and lubricate swing bearings weekly.
- Thoroughly clean and lubricate undercarriage rollers monthly, or more often in difficult conditions.
For older used excavators, increase lubrication frequency, and consider investing in premium-grade greases to further reduce wear.
If your used excavator develops unusual sounds, joint stiffness, or rapid wear:
- Check for evidence of poor lubrication: dry, squeaky joints or excessive play in moving parts.
- Remove old grease and clean fittings before re-lubricating.
- Examine for seal failure, which can allow contaminants entry and lead to major repairs.
Staying vigilant will maximize uptime and minimize costly breakdowns in a fleet of used excavators.
Operators looking to refine their greasing habits can:
- Switch to automatic lubrication systems for consistent, hands-free operation, especially in larger fleets of used excavators.
- Use color-coded maintenance logs to track greasing frequency and reduce missed intervals.
- Consult with lubricant specialists to tailor product selection for specific operating environments, further improving equipment reliability.
Applied correctly, advanced greasing helps used excavators retain value, run smoother, and endure extended operational periods. Key recommendations:
- Always choose high-quality, reputable products formulated for extreme load and environmental resistance.
- Maintain detailed records of all greasing and maintenance activities.
- For storage or extended downtime, apply water-resistant grease to all exposed points and operate the machine briefly to distribute lubricant evenly.
Built-in diligence safeguards investments and helps establish a reputation for reliability in heavy equipment supply and services.
Greasing is a critical aspect of maintaining a used excavator, directly impacting its productivity, safety, and longevity. By selecting appropriate grease types and adhering to consistent application routines, operators can diminish the risks of mechanical failure and stretch the machine's useful life. KeyChain Venture Co., Ltd. remains committed to providing robust commercial vehicle solutions characterized by durability, reliability, and ease of maintenance. Prioritizing effective lubrication will ensure your fleet of used excavators delivers exceptional value through every project and operational cycle.
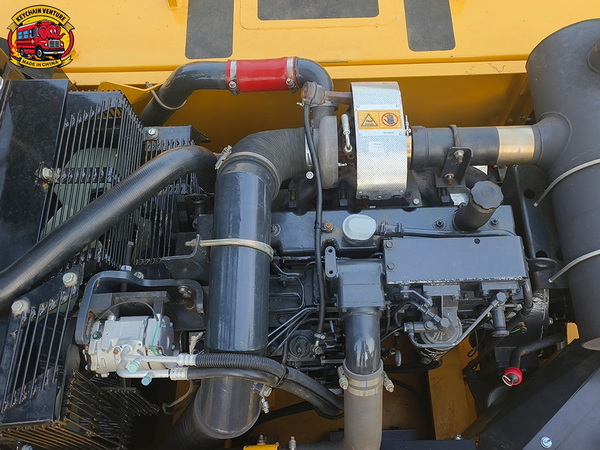
A high-quality lithium complex grease with EP additives suits most excavator components, while molybdenum disulfide grease offers enhanced protection for high-load joints like boom and bucket pins.
Daily greasing is ideal during heavy use, and at least once per week during lighter operation. Older excavators or those operating in tough environments may require increased frequency.
Yes, using incorrect grease can lead to increased friction, rapid wear, and possible component failure. Always follow manufacturer instructions.
Greasing all moving joints prior to storage prevents rust, corrosion, and contamination, especially if the equipment will be in humid or outdoor settings.
Check for fresh lubricant extrusion, smooth movement, and quiet operation at all joints. Perform routine inspections and document maintenance for proof of proper care.
Field Visit To DR Congo – Products in Action, Friendships in Progress
Treat Your Team to the Perfect Ending: A Cultural Day & Rejuvenating Massage
Just received this absolutely gorgeous bouquet specially ordered by our lovely customer!
Truly inspiring conversations today with our highly insightful client!
Today, we visited the bus company together with our client. It was really wonderful!
A Milestone Moment: Custom Buses Successfully Shipped, Setting Course for New Horizons
Forging Stronger Ties: Welcoming Key African Partners to Chongqing for Transport Collaboration